LeetCode Problems Tracker
LeetCode Problems Tracker
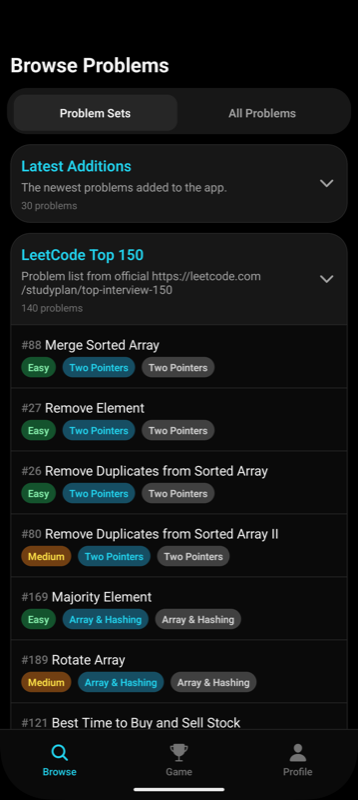
Мобильное приложение для решения и отслеживания прогресса по топ-100 задачам LeetCode.
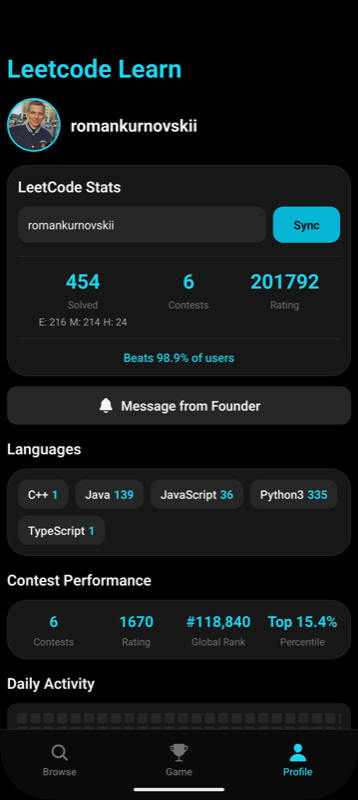
- 📈 Отмечайте прогресс по каждой задаче
- 📝 Читайте подробные решения и объяснения
- 🌍 Доступно на русском и английском языках
- 🏆 Сфокусировано на самых важных задачах LeetCode для собеседований и обучения
Попробуйте сейчас:
Это мобильное приложение создано для тех, кто готовится к техническим собеседованиям или хочет прокачать алгоритмические навыки. Отмечайте решённые задачи, читайте подробные разборы и поддерживайте мотивацию, проходя лучшие задачи LeetCode!
Platforms: android, ios
