Encrypting S3 Objects Using SSE-KMS
On This Page
Lab
Creating a Customer Master Key (CMK)
1. In the AWS Management Console search bar, enter KMS, and click the KMS result under Services:

2. Select Customer managed****keys in the left pane of the KMS console.
Warning: Cloud Academy cleans up the lab environment for you after a lab is completed or terminated. As a precaution, AWS prevents keys from being deleted immediately. Rather, they are queued for deletion, and an expiration period is set (of 7-30 days). For this reason, you may see residual keys from other students within the last week. For this reason, you may need to append a unique number to the Alias field in the next instruction.
3. Click Create Key, then expand Advanced Optionsand set the following values:
- Key type: Symmetric(Symmetric keys are suitable for most data encryption applications. The same key is used for both encrypt and decrypt operations with symmetric key algorithms.)
- Key usage: Encrypt and decrypt
- Advanced options:
- Key Material Origin: Leave as KMS (default). AWS will generate the key material for encryption. Note that another common use case is for customers to generate their own keys, and have AWS keep a back up encrypted copy and help manage them with KMS.
- Regionality:Single-Region key

4. Click Next to advance to the Add Labels page of the wizard.
5. Set the following values before clicking Next (leave the default values for other fields)
- Alias: calabs-CMK-key(Append a unique number to the key’s Alias if needed to be unique. For example, calabs-CMK-key2.)
- Description:
6. Click Next to advance to Define Key Administrative Permissions and leave the default values.
Administrative permissions allow users and roles to administer CMKs but not to perform cryptographic operations. In production environments, this is sometimes used to easily grant limited access to other users. The Allow key administrators to delete this keycheckbox makes it explicit if deleting keys is allowed, since the key can’t be recovered once deleted, making recovery of encrypted data impossible. Note that key deletion is not immediate and first enters into a pending state before the key is deleted. The delete operation can be canceled while in the pending state.
These settings generate a key policy. The default policy allows IAM policies to grant access the key, which is why you don’t require selecting your student user as an administrator. The lab IAM policy of your student user allows you to perform the required actions of the lab.
7. Click Next to advance to Define Key Usage Permissions.
Usage permissions grant access to perform cryptographic operations such as encrypting and decrypting. Enterprises usually have different permissions for administrators and users, hence the wizard walks you through defining both.
Notice that you can grant access to the key so other AWS accounts can use it for encryption/decryption.
8. Click Nextto preview the key policy and then click Finish when ready.
The CMK is created.
9. Confirm the key created correctly and that the Status is Enabled:

Encrypting S3 Data using Server-Side Encryption with KMS Managed Keys (SSE-KMS)
You will upload a file and encrypt it using SSE-KMS in this lab step.
1. In the AWS Management Console search bar, enter S3, and click the S3 result under Services:

2. Click the name of the bucket the Cloud Academy lab environment created for you (name begins with cloudacademylabs-ssekms):

3. Click Upload.
4. Click Add files and select a small file, or download this sample file and select it.
5. Expand the Properties tab and scroll until the Server-side encryption settings.
6. Check the Specify an encryption key checkbox.
7. Check the AWS Key Management Service key (SSE-KMS) checkbox and then the Choose from your AWS KMS keys checkbox:

8. Choose the AWS KMS key you previously generated:

9. Click on Upload.
10. Click Close and then click the name of the object to open its properties panel:

You can verify the object is encrypted using SSE-KMS by checking that the Encryption field is AWS-KMS.
Enforcing S3 Encryption Using Bucket Policies
1. In the S3 bucket console, click the Permissions tab followed by Bucket Policy to open the Bucket policy editor:
Bucket policies are IAM policies applied to a bucket rather than to a user or role as is conventionally done with IAM policies. Similar to how a key policy applied to the CMK. These are examples of resource-based policies in AWS.
2. Paste the following bucket policy into the policy editor:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Id": "RequireSSEKMS",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "DenyUploadIfNotSSEKMSEncrypted",
"Effect": "Deny",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": "s3:PutObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::<Your_Bucket_Name>/*",
"Condition": {
"StringNotEquals": {
"s3:x-amz-server-side-encryption": "aws:kms"
}
}
}
]
}
This policy denies ("Effect": "Deny") all users’ ("Principal": "*") uploads ("Action": "s3:PutObject") to the bucket ("Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::<Your_Bucket_Name>/*") if the s3:x-amz-server-side-encryption is not set to aws:kms, which corresponds to SSE-KMS. The lab provides you with the policy but you could recreate it using the policy generator linked to beneath the policy editor.
3. Replace <Your_Bucket_Name> with the name of your lab bucket (it begins with cloudacademylabs-ssekms- and can be copied from the S3 console):
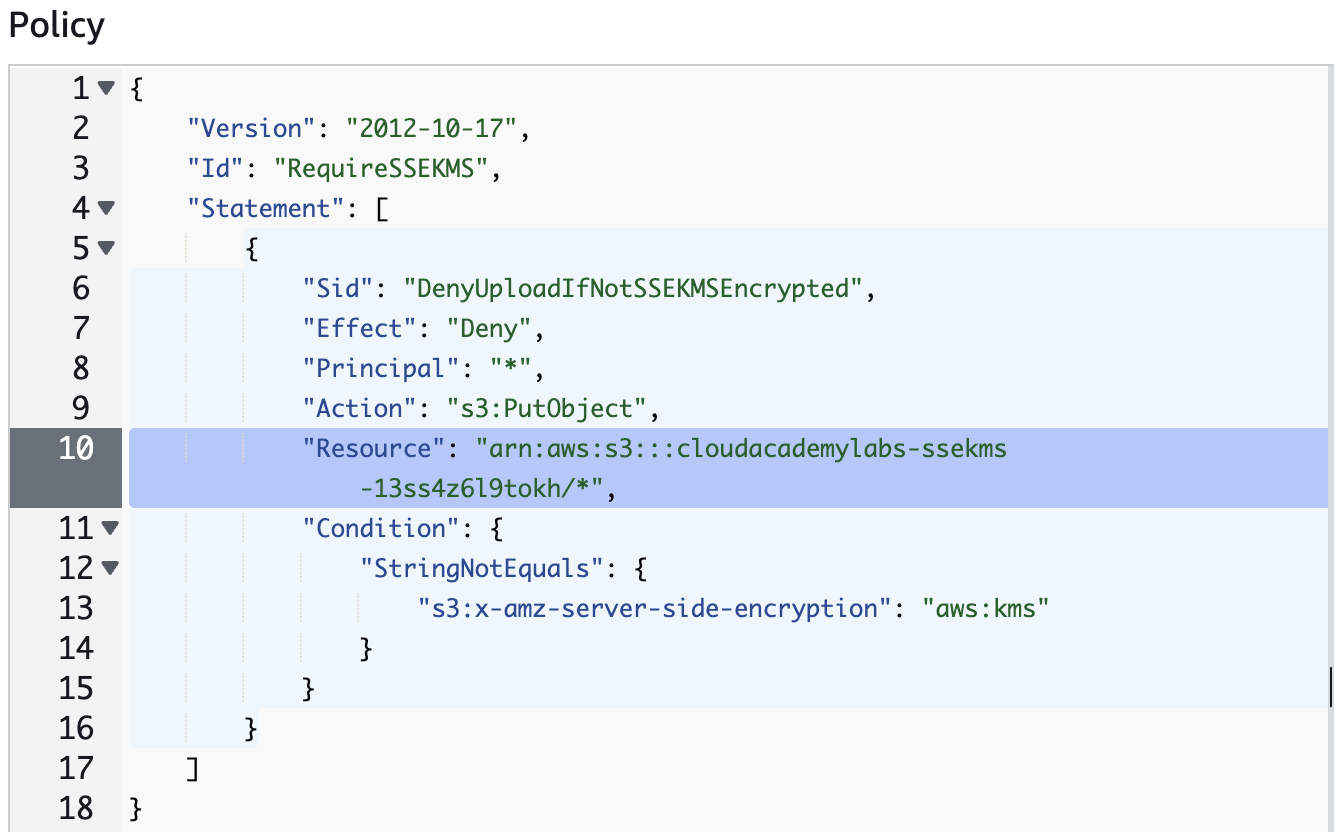
4. Click Save changes to save the policy and have it start being enforced.
5. Click the Objectstab followed by Upload.
6. Click Add files and select a small file, or download this sample file and select it.
7. Click Upload and observe the image does not appear in the bucket contents table.
Clicking upload without configuring any properties of the object uses the default of no encryption.
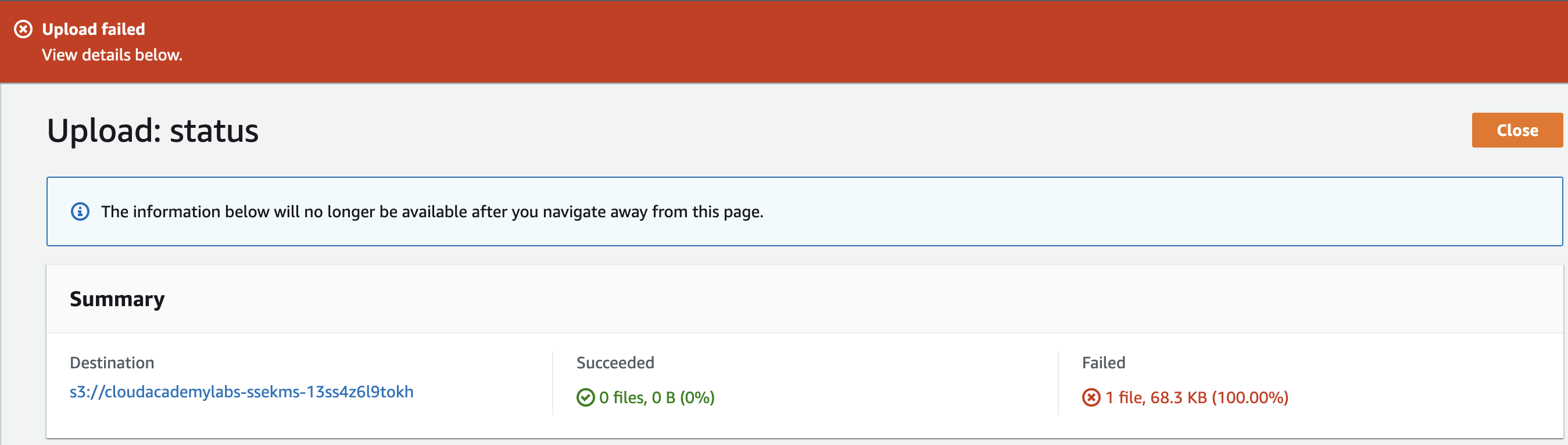
You can see the upload Failed.
8. Retry the upload but this time use the Set properties step to configure Encryptionto AWS KMS master-key using your CMK.
The upload now succeeds since the bucket policy condition is satisfied:

The policy does not require the use of your CMK however, so the default S3 KMS key in the region is also allowed. You can change the policy condition to enforce a specific CMK is used.