Key Management Service
On This Page
About
AWS Key Management Service (KMS) makes it easy for you to create and manage cryptographic keys and control their use across a wide range of AWS services and in your applications.
AWS KMS provides management of encryption keys for use with other AWS services (e.g. EBS, S3, RDS, etc.).
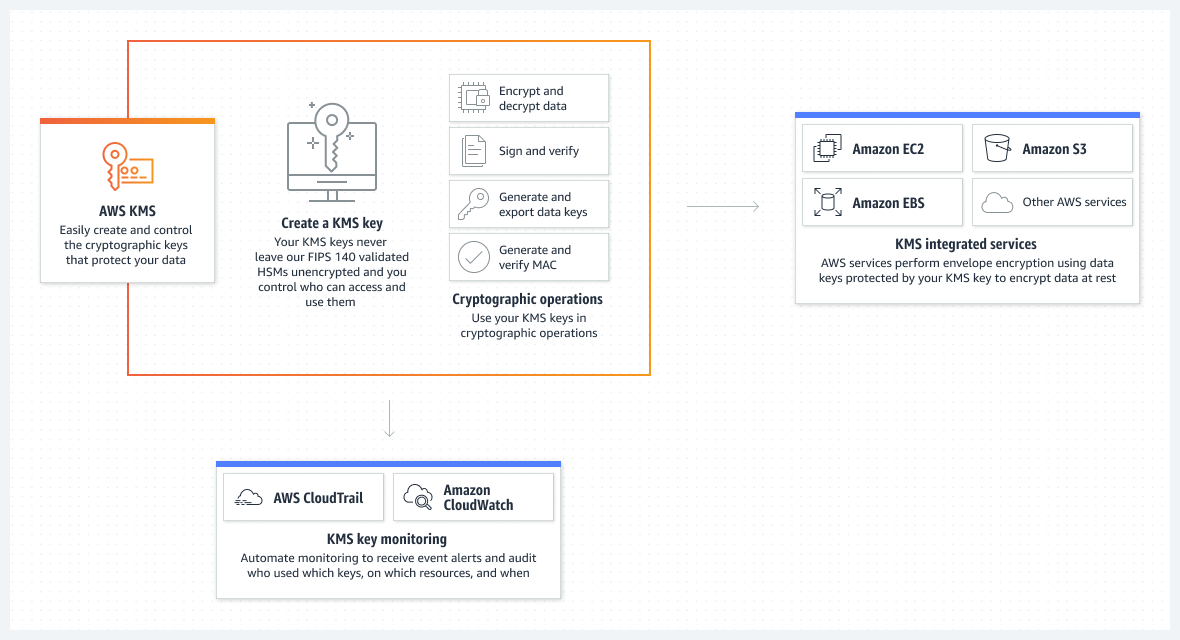
Key management on AWS is a broad range of activities from creating & storing public & private keys to creating, managing, and authorising access to AWS services with digital keys. This guide explains the key management solution on AWS that is easiest to use, most secure, and provides the most flexibility for you to create and manage your keys the way you need them.
Alternatives
- HashiCorp Vaultc
- Azure Key Vault
- Google Cloud Key Management Service
- OpenSSH
- Akeyless Vault Platform
- Virtru
Concepts
Key types:
- Customer managed keys
- AWS managed keys
- AWS owned keys
In May 2022, AWS KMS changed the rotation schedule for AWS managed keys from every three years (approximately 1,095 days) to every year (approximately 365 days)
| Type of KMS key | Can view KMS key metadata | Can manage KMS key | Used only for my AWS account | Automatic rotation | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer managed key | Yes | Yes | Yes | Optional. Every year (approximately 365 days) | Monthly fee (pro-rated hourly) Per-use fee |
| AWS managed key | Yes | No | Yes | Required. Every year (approximately 365 days) | No monthly fee Per-use fee (some AWS services pay this fee for you) |
| AWS owned key | No | No | No | Varies | Varies |
Customer Managed Keys (CMK)
The primary resources in AWS KMS are customer master keys (CMKs). Typically, you use CMKs to protect data encryption keys (or data keys) which are then used to encrypt or decrypt larger amounts of data outside of the service. CMKs never leave AWS KMS unencrypted, but data keys can. AWS KMS does not store, manage, or track your data keys.
There is one AWS-managed CMK for each service that is integrated with AWS KMS. When you create an encrypted resource in these services, you can choose to protect that resource under the AWS-managed CMK for that service. This CMK is unique to your AWS account and the AWS region in which it is used, and it protects the data keys used by the AWS services to protect your data.
Data keys
Data keys are used to encrypt large data objects within an application outside AWS KMS.
Key rotation and Backing Keys
When you create a customer master key (CMK) in AWS KMS, the service creates a key ID for the CMK and key material, referred to as a backing key, that is tied to the key ID of the CMK. If you choose to enable key rotation for a given CMK, AWS KMS will create a new version of the backing key for each rotation. It is the backing key that is used to perform cryptographic operations such as encryption and decryption. Automated key rotation currently retains all prior backing keys so that decryption of encrypted data can take place transparently. CMK is simply a logical resource that does not change regardless of whether or of how many times the underlying backing keys have been rotated.
A KMS key consists of
- Alias
- Creation date
- Description
- Key state
- Key material (either customer provided or AWS provided)
A KMS key can:
- encrypt data up to 4KB in size
- generate, encrypt, and decrypt Data Encryption Keys (DEKs)
- never be exported from KMS (CloudHSM allows this).
Aliases
Use an alias as a friendly name for a KMS key. For example, you can refer to a KMS key as test-key instead of 1234abcd-12ab-34cd-56ef-1234567890ab.
Custom key stores
A custom key store is an AWS KMS resource associated with FIPS 140-2 Level 3 hardware security modules (HSMs) in a AWS CloudHSM cluster that you own and manage.
Key policy
When you create a KMS keys, you determine who can use and manage that KMS keys.
Digest
- KMS encrypts small pieces of data (usually data keys) MAX - 4 KB
- Use Envelope Encryption for larger objects (CMK never leaves KMS)
- Generate a data key (plain-text and encrypted) from KMS (GenerateDataKey)
- Use data key to perform encryption/decryption on the object (within the service or client-side)
- Use Envelope Encryption for larger objects (CMK never leaves KMS)
- You can assign an encryption context with cryptographic operations
- If encryption context is different, decryption will NOT succeed
- Request quotas for KMS Cryptographic operations:
- 5,500 to 50,000 per second (varies with Region)
- You might get a ThrottlingException if you exceed the limit
- Lower your request rate to AWS KMS or Retry with Exponential Backoff
- Usage of KMS CMKs can be tracked in CloudTrail
- Key policies control access to CMKs (incl. cross account access)
- Use AWS Encryption SDK to interact with KMS(Provides Data Key Caching)
Price
KMS vs Cloud HSM
- Generate, store, use and replace your keys(symmetric & asymmetric)
- KMS: Multi-tenant Key Management Service
- KMS integrates with all storage and database services in AWS
- Define key usage permissions (including cross account access)
- Automatically rotate master keys once a year
- Schedule key deletion to verify if the key is used
- Mandatory minimum wait period of 7 days (max-30 days)
- CloudHSM: Dedicated single-tenant HSM for regulatory compliance
- AWS KMS is a Multi-tenant service
- AWS CANNOT access your encryption master keys in CloudHSM
- (Recommendation) Be ultra safe with your keys. Use two or more HSMs in separate AZs.
- AWS KMS can use CloudHSM cluster as “custom key store” to store the keys:
- AWS Services can continue to talk to KMS for data encryption
- (AND) KMS does the necessary integration with CloudHSM cluster
Use Cases
Type: Data protection
Same type services: Macie, Key Management Service (KMS), CloudHSM, Certificate Manager, Secrets Manager
CloudHSM: (Web servers) Offload SSL processing, Certificate Authority etc
Practice
How to encrypt S3 Objects Using SSE-KMS
Questions
Q1
Key rotation is an important concept of key management. How does Key Management Service (KMS) implement key rotation?
- KMS supports manual Key Rotation only; you can create new keys any time you want and all data will be re-encrypted with the new key.
- KMS creates new cryptographic material for your KMS keys every rotation period, and uses the new keys for any upcoming encryption; it also maintains old keys to be able to decrypt data encrypted with those keys.
- Key rotation is the process of synchronizing keys between configured regions; KMS will synchronize key changes in near-real time once keys are changed.
- Key rotation is supported through the re-importing of new KMS keys; once you import a new key all data keys will be re-encrypted with the new KMS key.
Explanation
When you enable automatic key rotation for a customer-managed KMS key, AWS KMS generates new cryptographic material for the KMS key every year. AWS KMS also saves the KMS key’s older cryptographic material so it can be used to decrypt data that it has encrypted.
Q2
Alan is managing an environment with regulation and compliance requirements that mandate encryption at rest and in transit. The environment covers multiple accounts (Management, Development, and Production) and at some point in time, Alan might need to move encrypted snapshots and AMIs with encrypted volumes across accounts.
Which statements are true with regard to this scenario? (Choose 2 answers)
- Create Master keys in management account and assign Development and Production accounts as users of these keys, then any media encrypted using these keys can be shared between the three accounts.
- Can share AMIs with encrypted volumes across accounts, even with the use of custom encryption keys.
- Make encryption keys for development and production accounts then anything encrypted using these keys can be moved across accounts.
- You can not move encrypted snapshots across accounts if data migration is required some third-party tools must be used.