ElastiCache
On This Page
About
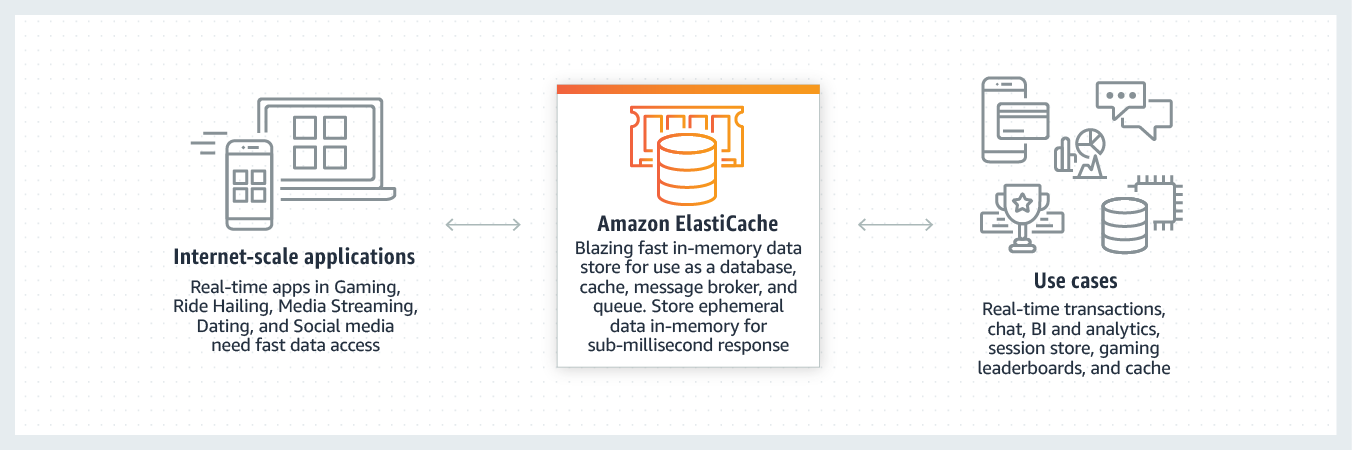
Amazon Elasticache is a fully managed Redis or Memcached in-memory data store.
It’s great for use cases like two-tier web applications where the most frequently accesses data is stored in ElastiCache so response time is optimal.
You can use ElastiCache for caching, which accelerates application and database performance, or as a primary data store for use cases that don’t require durability like session stores, gaming leaderboards, streaming, and analytics.
Compatible with Redis and Memcached
Price
Use Cases
Type: In-memory
| Use Case | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Web session store | In cases with load-balanced web servers, store web session information in Redis so if a server is lost, the session info is not lost, and another web server can pick it up |
| Database caching | Use Memcached in front of AWS RDS to cache popular queries to offload work from RDS and return results faster to users |
| Leaderboards | Use Redis to provide a live leaderboard for millions of users of your mobile app |
| Streaming data dashboards | Provide a landing spot for streaming sensor data on the factory floor, providing live real-time dashboard displays |
Caching Engines
| Memcached | Redis |
|---|---|
| Simple, no-frills | You need encryption |
| You need to elasticity (scale out and in) | You need HIPAA compliance |
| You need to run multiple CPU cores and threads | Support for clustering |
| You need to cache objects (e.g. database queries) | You need complex data types |
| You need HA (replication | Backup and restore features |
| Pub/Sub capability | Multi-AZ with Auto-Failover |
| Non persistent. No backups | |
| Multi-node for partitioning of data (sharding) |
Memcached
ElastiCache manages Memcached nodes as a pool that can grow and shrink (similar to an EC2 Auto Scaling group); individual nodes are expendable and non-persistent.
Memcached provides a simple caching solution that best supports object caching and lets you scale out horizontally. Ideal for offloading a DB’s contents into a cache.
Redis
ElastiCache manages Redis more as a relational database, i.e. Redis clusters are managed as persistent, stateful entities that include using multi-AZ redundancy for handling failover (similar to RDS).
Redis supports complex data structures, hence would be ideal in cases where sorting and ranking datasets in memory are important (e.g. such as in leaderboards for games).
Caching Strategies
Lazy Loading
- The data that is read from the DB is stored in the cache. The data can become stale
- The data becomes stale because there are no updates to the cache when data is changed in the database
Only cache data when it is requested. Cache miss penalty on initial request. Chance to produce stale data; can be mitigated by setting a TTL. Shorter TTL = less stale data.
Write-Through
- The data is added/updated into the cache everytime the data is written to the DB (no stale data)
- Because the data in the cache is updated every time it’s written to the database, the data in the cache is always current.
Every database write will write to the cache as well. Data is never stale however there will be alot more operations to perform; and these resources are wasted if most of the data is never used.
Session Store
- Stores temporary session data in cache (with TTL) - Time to Live. Data expires after the given time
Practice
Configuring a Lambda function to access Amazon ElastiCache in an Amazon VPC
Questions
Q1
What is one reason that AWS does not recommend that you configure your ElastiCache so that it can be accessed from outside AWS?
- The metrics reported by CloudWatch are more difficult to report.
- Security concerns and network latency over the public internet.
- The ElastiCache cluster becomes more prone to failures.
- The performance of the ElastiCache cluster is no longer controllable.
Explanation
Elasticache is a service designed to be used internally to your VPC. External access is discouraged due to the latency of Internet traffic and security concerns. However, if external access to Elasticache is required for test or development purposes, it can be done through a VPN.
2
Q2
You are building a web application that will run in an AWS ElasticBeanstalk environment. You need to add and configure an Amazon ElastiCache cluster into the environment immediately after the application is deployed.
What is the most efficient method to ensure that the cluster is deployed immediately after the EB application is deployed?
- Use the AWS Management Console to create and configure the cluster.
- Create a cron job to schedule the cluster deployment using the aws cloudformation deploy command
- Create a configuration file with the .config extension and place it into the .ebextensions folder in the application package.
- Build an AWS Lambda function that polls to the ElasticBeanstalk environment deployments and create and configure the Amazon ElastiCache cluster.