CloudFront
![[aws CloudFront]](https://cdn.worldvectorlogo.com/logos/aws-cloudfront.svg)
On This Page
About
Securely deliver data, videos, applications, and APIs to customers globally with low latency, and high transfer speeds
CloudFront is a distributed content delivery network (CDN) that enables easy delivery of web content to end users from a pool of web servers around the globe
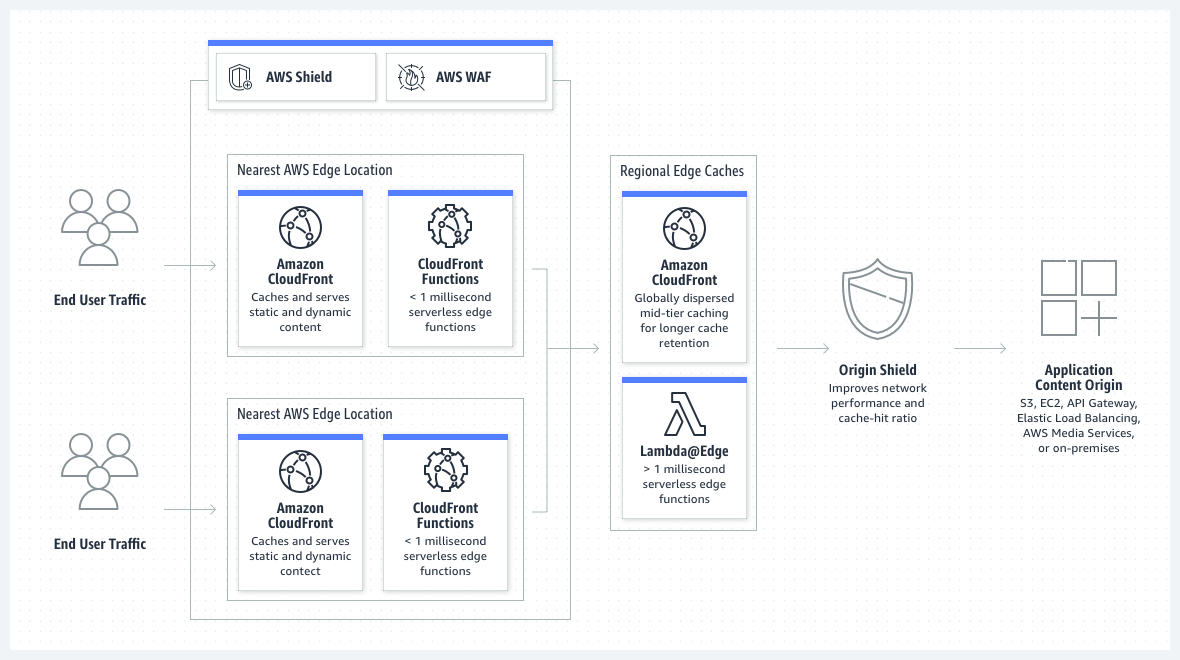
CloudFront is a global service:
- Ingress to upload objects.
- Egress to distribute content.
Terminology
- Edge Location: The location where content is cached to be accessed by users. These are READ/WRITE.
- CDN: A collection of Edge Locations that can distribute content around the world.
- Origin: The origin of all files the CDN will distribute. E.g.
- an S3 bucket hosting some images, or hosting a static website
- an EC2 instance running a website with dynamic content
- an ELB pointing to several EC2 instances
- a DNS endpoint using Route53
- any origin server, even non-AWS
- Distribution: The name of the CDN.
- Web Distribution: Used for delivering content over HTTP/HTTPS. Can be either an S3 bucket or a web server (EC2/non-AWS). Cannot serve multimedia content.
- RTMP Distribution: Uses RTMP for media streaming and flash multimedia content. Probably what Netflix uses.
Price
There is an option for reserved capacity over 12 months or longer (starts at 10TB of data transfer in a single region).
| Pay | do not pay |
|---|---|
| Data Transfer Out to Internet | Data transfer between AWS regions and CloudFront. |
| Data Transfer Out to Origin | Regional edge cache. |
| Number of HTTP/HTTPS Requests | AWS ACM SSL/TLS certificates. |
| Invalidation Requests | Shared CloudFront certificates. |
| Dedicated IP Custom SSL | |
| Field level encryption requests |
Use Cases
Type: Content delivery networks
Practice
Configuring a Static Website With S3 And CloudFront
Questions
Q1
A company with global users is using a content delivery network service to ensure low latency for all customers. The company has several applications that require similar cache behavior.
Which API command can a developer use to ensure cache storage consistency with minimal duplication?
- A) CreateReusableDelegationSet with Route 53
- B) CreateStackSet with CloudFormation
- C) CreateGlobalReplicationGroup with ElastiCache
- D) CreateCachePolicy with CloudFront
Q2
A developer is designing a web application that allows the users to post comments and receive in a real-time feedback.
Which architectures meet these requirements? (Select TWO.)
- Create an AWS AppSync schema and corresponding APIs. Use an Amazon DynamoDB table as the data store.
- Create a WebSocket API in Amazon API Gateway. Use an AWS Lambda function as the backend and an Amazon DynamoDB table as the data store
- Create an AWS Elastic Beanstalk application backed by an Amazon RDS database. Configure the application to allow long-lived TCP/IP sockets.
- Create a GraphQL endpoint in Amazon API Gateway. Use an Amazon DynamoDB table as the data store.
- Enable WebSocket on Amazon CloudFront. Use an AWS Lambda function as the origin and an Amazon Aurora DB cluster as the data store
Explanation
AWS AppSync simplifies application development by letting users create a flexible API to securely access, manipulate, and combine data from one or more data sources. AWS AppSync is a managed service that uses GraphQL to make it easy for applications to get the exact data they need.
AWS AppSync allows users to build scalable applications, including those requiring real-time updates, on a range of data sources, including Amazon DynamoDB. In Amazon API Gateway, users can create a WebSocket API as a stateful frontend for an AWS service (such as AWS Lambda or DynamoDB) or for an HTTP endpoint.
The WebSocket API invokes the backend based on the content of the messages it receives from client applications. Unlike a REST API, which receives and responds to requests, a WebSocket API supports two-way communication between client applications and the backend.
1, 2