LeetCode Problems Tracker
LeetCode Problems Tracker
A mobile app to help you solve and track your progress on the top 100 LeetCode problems.
- 📈 Track your progress on each problem
- 📝 Read clear solutions and explanations
- 🌍 Available in English and Russian
- 🏆 Focus on the most important LeetCode problems for interviews and learning
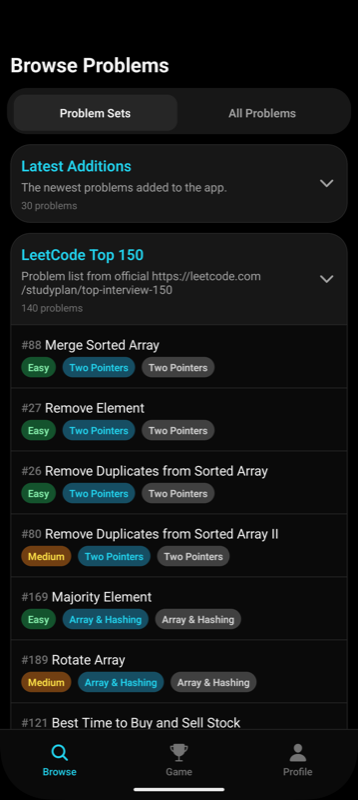
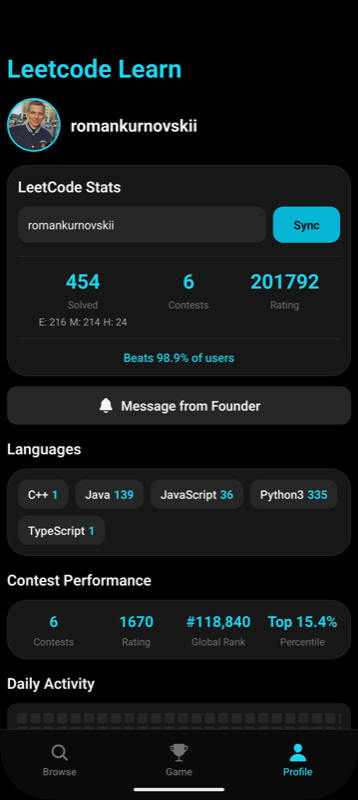
Try it now:
This mobile app is designed for anyone preparing for coding interviews or looking to improve their algorithm skills. Mark problems as solved, read detailed solutions, and keep your motivation high as you work through the best of LeetCode!
Platforms: android, ios
